If you’re in Finance, you’ve likely been following the adoption of cryptocurrencies by financial firms worldwide. You’ve also probably noticed that their proponents argue that Bitcoin is just the tip of the Decentralized Finance (DeFi) iceberg.
DeFi is an incredibly diverse, crazily entertaining space. However, it can also feel like a chore to get up to speed regarding all the different terms, ideas, and innovations happening within it. In this article, we’ll get you up on the right foot, taking advantage of your existing knowledge.
Just beware: You might end up wearing a unicorn t-shirt.
Getting started with Decentralized Finance (DeFi Explained)
DeFi is, in short, the attempt to create a new financial ecosystem that’s based on decentralized alternatives on the blockchain. Therefore, it relies heavily on smart contracts (which are, basically, code but on the blockchain) and P2P transactions. Many exemplify DeFi using the meme ‘money LEGOs’, referring to how projects on Ethereum can interact and build on top of one another.
PRO TIP! If you don’t understand what any of this means, you can check out our 2021 Institutional Blockchain Investment Guide, where we go deep into these topics, from blockchains to investing legally in crypto.

The road to adoption of DeFi by the masses has been paved with a series of milestones such as the origins of lending protocols, improvement of Decentralized Exchanges (DEXs), the launching of sophisticated tools that allow any web developer to program smart contracts (such as Metamask), the launch of insurance systems in DeFi, among other key moments. In this section, we will cover the importance and workings of DeFi, and will analyse how it can help us re-conceptualize the entire financial system as we know it, put entirely on blockchains.
What Is DeFi? Basic Concept And Benefits.
DeFi is also known as Distributed Finance, or Open Finance in China. At its purest level, DeFi proposes the creation of a financial business environment without any central endorsement body. Instead, DeFi proposes mechanisms to create this financial system through an open-source, permissionless, and decentralized system based on programmable blockchains with the ability to store and execute smart contracts, such as Ethereum, which hosts most DeFi protocols. Since anyone can interact with public blockchains, the financial applications hosted within them are permissionless. Furthermore, all smart contracts reside on the same system, allowing the sharing of data to be seamless.
Since the blockchain has created the possibility to digitalize all kinds of assets, DeFi isn’t limited to cryptocurrencies in the traditional sense, but to all valuable assets. In theory, any valuable asset could be posted to a smart contract and be subject to coded financial mechanisms.
Apart from the aforementioned benefits of being hosted in blockchains, there are a series of additional perks that DeFi has over traditional finance (TradFi), namely:
- Extremely low overhead.
- DeFi doesn’t need to conduct background checks or due diligence or ask parties for any additional information, since all contracts are programmed and executed by code.
- The algorithms that govern DeFi are infinitely adaptable and run 24/7, making the system capable of determining fees, rates, etc. by itself.
- Given that cryptocurrencies are highly liquid and easily interchangeable, protocols that prove themselves can, potentially, attract the whole markets’ worth of funds.
- The programmable nature of DeFi protocols allows them to easily interact with each other to leverage their multiple strengths.
Don’t believe us when it comes to how DeFi is on track to disrupting finance? See our podcast chat with EQIBank’s CEOs to learn why they decided to move their bank over to DeFi!
DeFi As The Financial Extension Of Blockchain 1.0
Blockchain 1.0 corresponds to the most primitive use cases of blockchains, exemplified by Bitcoin. Blockchain 1.0 serves the function of circulating assets through distributed ledgers, chain data and consensus algorithms.
The ultimate promises of Blockchain 1.0 are:
- Absolute decentralization.
- High transparency.
- Pseudonym authentication
Blockchain 1.0’s innovation was proposing decentralized solutions to financial issues, with pseudonymous payments and custody of digital currencies, based on ideas of free currency economics.
This stage of blockchain development does not contemplate more complex solutions, such as a financial landscape and the programmability of money. Because of this, DeFi represents an advance from Blockchain 1.0’s theoretical basis.
How DeFi Resembles And Improves On Traditional Finance
Traditional finance is built on trust while DeFi is built on code. Every facet of the modern financial system is still based on trust directly or indirectly.
With the popularization of electronic technology and information systems, data-based analysis and evaluation of credit, the timeless trust process that governs these systems from their start has been optimized and improved upon, but never fully replaced by trustless alternatives.
After the advent of blockchain technology, there is now a possibility to have completely transparent systems that can govern financial decisions under a “zero human intervention” principle. For example, to power a DeFi loan, there is no need for credit data and a trust relationship; through public consensus and rules and transparent code and procedures, both parties are able to transact. DeFi depends on the strength of its protocols, cryptography, and smart contracts, and the scale of its networks decides the stability of a system: The larger the network is, the more stable the system will be.
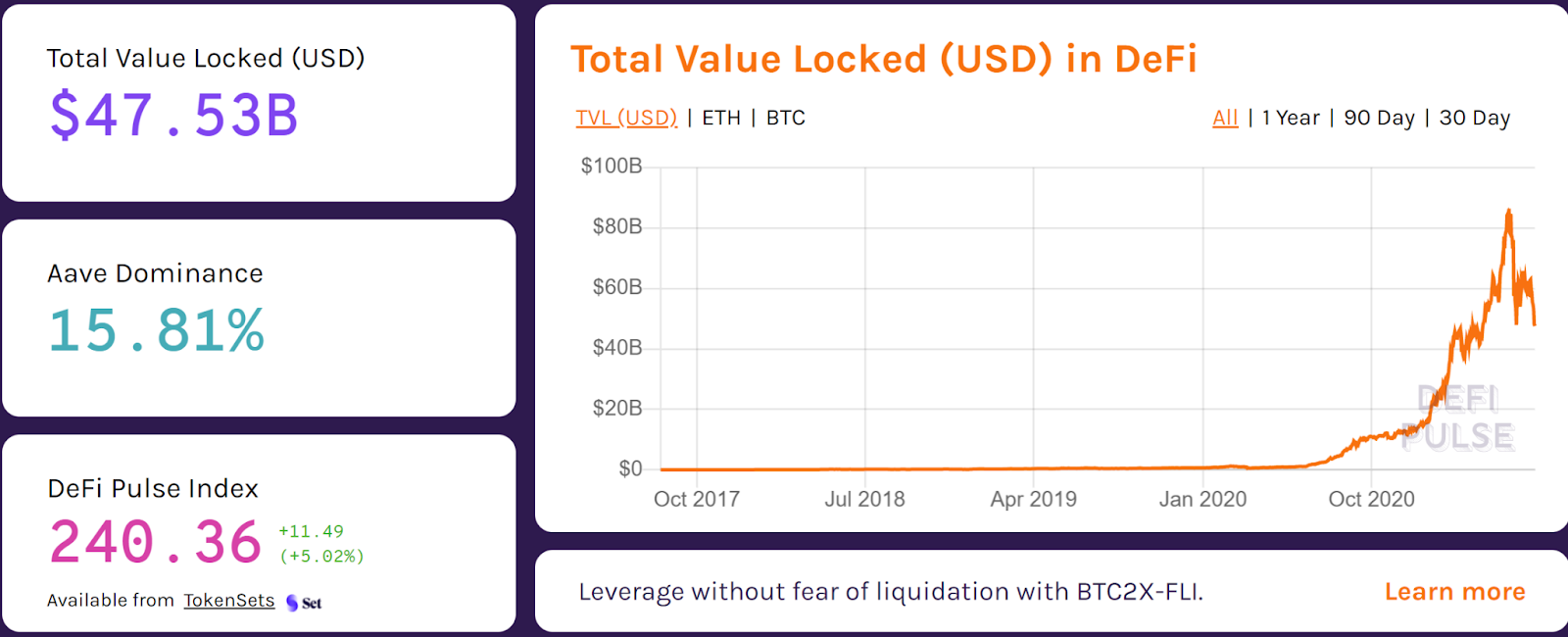
DeFi also allows small and bigger participants to participate equally. For example, some complex financial services rely on third-party rating agencies and similar financial institutions that can be “gamed” or corrupted, which DeFi can completely bypass using set, transparent systems and decentralized data oracles (a complex concept out of this article’s scope). Also, because of its composable and decentralized nature, cross-regional restrictions, peer-to-peer lending and peer-to-peer micropayments, as well as the issuing of complex financial instruments (which are limited in the traditional financial system), can all happen in DeFi.
The following image shows an overview and comparison of how different DeFi projects have launched on Ethereum, the most popular smart contracts platform and therefore the home of most DeFi protocols, to replace TradFi alternatives. It’s also important that you remember that, on the right side of the spectrum, alternatives can also easily plug and cooperate among each other, creating the possibility of near-instant synergies.
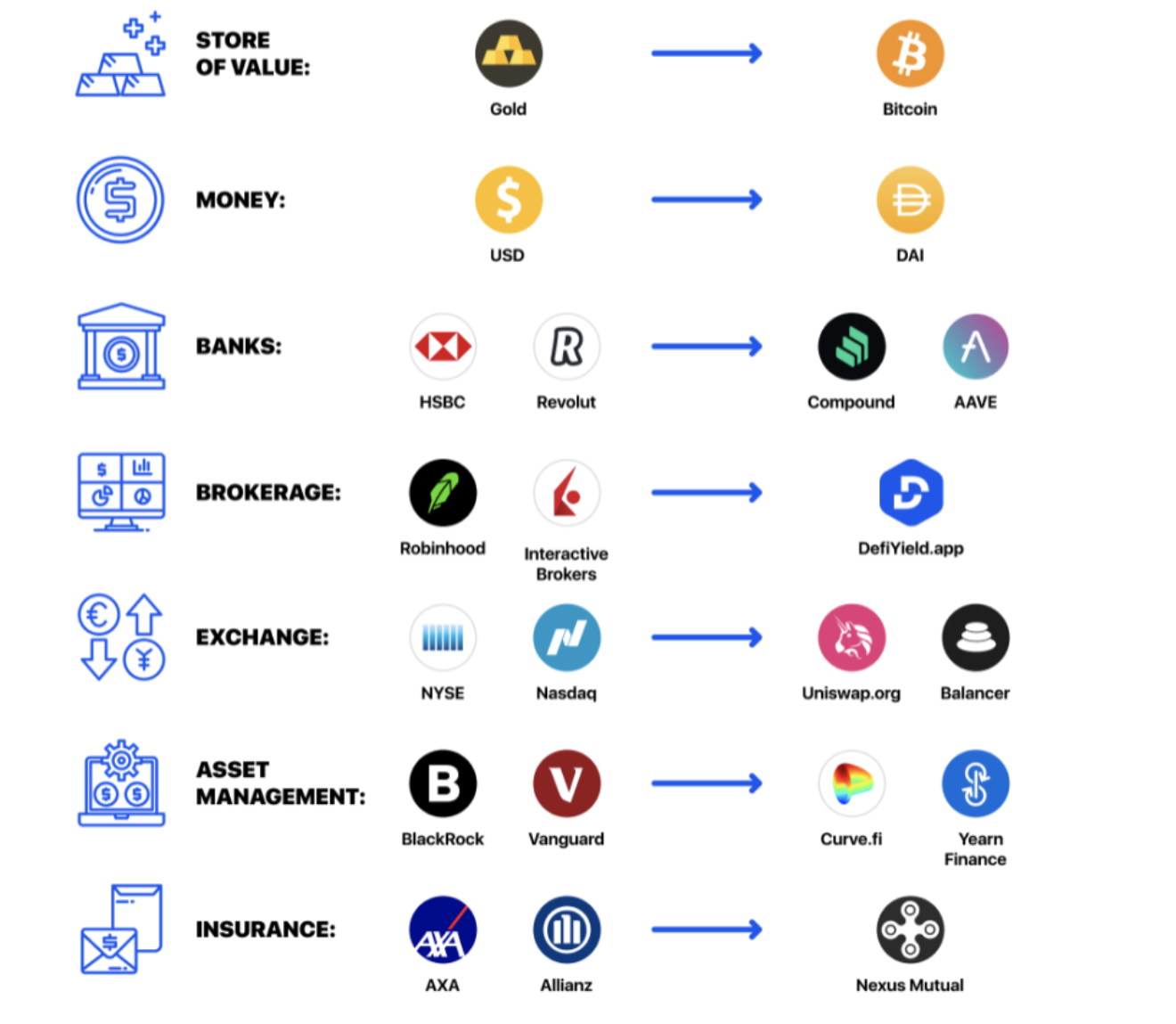
Protocols supported by DeFi include decentralized lending, decentralized exchanges, stablecoins (payments/assets), automated market making, currency locking in exchange for interest, liquidity providing, and other decentralized derivatives. The image below showcases how different projects based on Ethereum have launched to replace centralized alternatives:
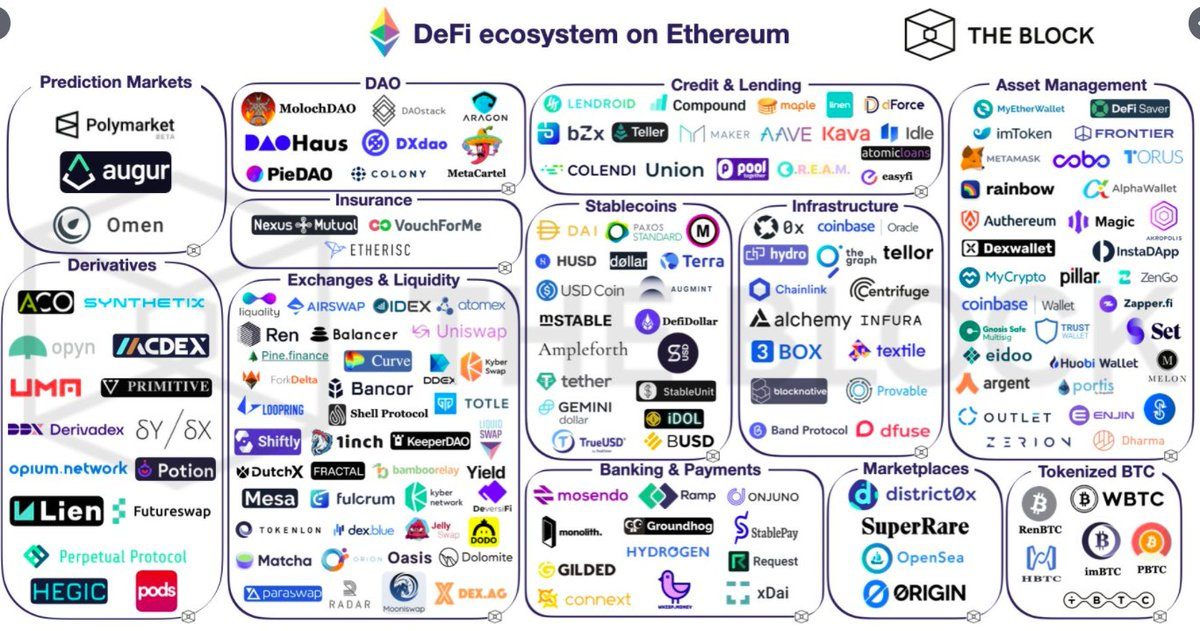
It’s also important, as you continue your trip through crypto land, to remember that given the open-source nature of blockchain and cryptocurrencies, anyone can create their own protocol to compete with Ethereum, and that projects can always migrate from it should they find a better alternative. This makes DeFi robust to either censorship or malfunction, eliminates single points of failure, and opens the door for new blockchains to launch with different sets of values that can compete with Ethereum. For example, both the Polkadot and the Tezos blockchains have been created by retired Ethereum founders to offer a different angle on smart contract platforms (the former having a focus on interoperability of different blockchains and the second one on scalability and speed).
There isn’t enough space in one article to cover the whole of DeFi. Because of this, we’d really insist that you grab a copy of our 2021 Institutional Investment Blockchain Guide for free, in which we cover these topics to a great extent.
We’re sure that, with a little help, you’ll be riding the blockchain waves pretty soon!